Are your sales reps struggling to close deals? You’re not alone. Many teams face this problem with upwards of 80% of new leads not converting into sales.
In most cases, the issue isn’t your skills—it could be the customers you’re speaking to. At least 50% of the prospects aren’t a good fit. Think of the time and energy it takes to qualify prospects. There’s an introductory call, email nurtures, and multiple meetings with decision-makers. It’s a big time investment and one you can’t afford.
This is where the MEDDIC methodology comes in handy. It takes a deep dive into the factors that drive purchasing decisions. It helps you understand the customer’s needs and motivations so you can prioritize buyers who are the best match, ensuring you fill your sales pipeline with the most promising opportunities. In this article, learn why MEDDIC is an excellent solution for sales qualification, practical tips, and whether it fits your organization.
What is MEDDIC Framework?
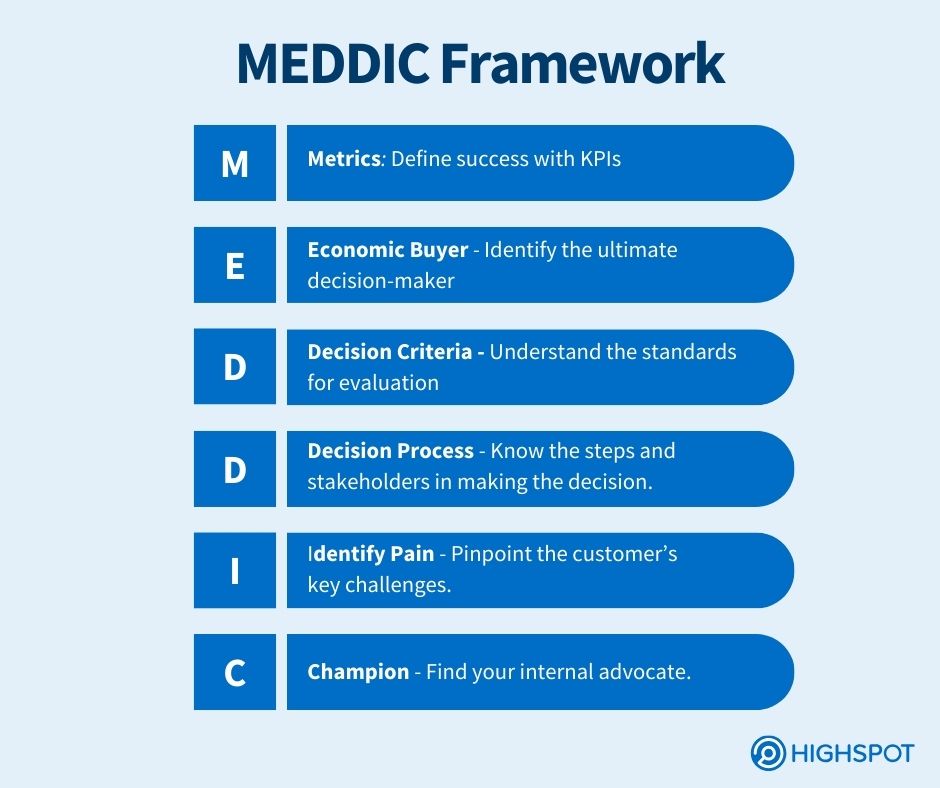
Meddic stands for Metrics, Economic Buyer, Decision Criteria, Identify Pain, and Champion. It’s a framework for qualifying and pursuing B2B sales leads that are more likely to convert.
It streamlines the sales process by guiding you on what questions to ask to find prospects who need your product. Not only does it help you close deals faster, but it also improves your sales forecast and maximizes your revenue potential. It works well in longer, complex sales cycles with multiple stakeholders.
John McMahon conceptualized MEDDIC sales methodology in the 1990s to improve lead qualification and sales processes at Parametric Technology Corporation (PTC). Dick Dunkel and Jack Napoli then documented and shared the framework throughout the company, integrating it into their onboarding and training programs and creating a common language for their revenue teams. This structured approach to sales qualification helped PTC boost its sales from $300 million to $1 billion.
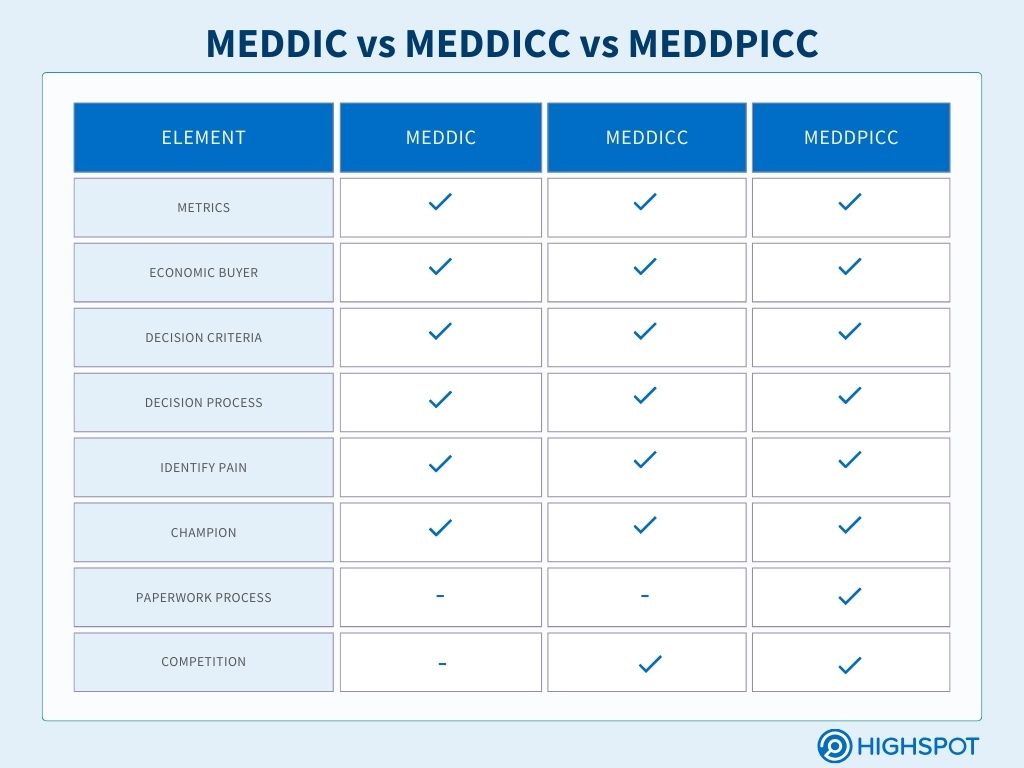
MEDDIC vs MEDDICC vs MEDDPICC
MEDDPICC and MEDDICC are variations of the original MEDDIC qualification framework. While they share core principles, each version has slight differences to address specific needs within the sales process.
MEDDPICC is considered the more modern and evolved version. It builds on the original principles by adding the paper process to help sales teams understand and navigate the customer’s procurement, legal processes, and competition to better understand and position solutions against competitors.
Below is a chart outlining the elements included in each framework:
The MEDDIC Sales Process
The MEDDIC sales qualification framework contains six elements to ensure no stone is left unturned when qualifying buyers. Each includes questions that help you determine whether the prospect is a good match for your solution. If they are, great, keep selling. If not, it’s likely time to move on to a more qualified lead.
Metrics
This component of MEDDIC measures the customer’s economic benefit. Simply, it’s the value your solution provides. For example, if a potential customer is intrigued by the support you offer because their current provider is unsatisfactory, create metrics that demonstrate your superior response and resolution times. This is an excellent opportunity to use case studies about customers with similar pain points or expectations to prove value.
- Discovery question example: “I’m curious, what does success look like for you and your team? Are there any specific KPIs or metrics you hope to improve with our solution?”
Economic Buyer
The economic buyer has the ultimate decision-making power and control over the budget. This person is usually higher up the company, such as a senior executive. In some cases, the economic buyer may be a group of decision-makers.
Identify the economic buyer early on. If possible, talk to them about their goals, priorities, and what they look for in a purchase. Otherwise, try to gather these details from your existing contact. Use what you learn to create an effective sales pitch that appeals to the economic buyer, even if they won’t be directly using your product or service.
- Discovery question example: “Who is your organization’s go-to person for this business area? Do they need to see the product before giving the green light? Do they sign off on the project?”
Decision Criteria
Buying decision criteria are the standards and specifications the customer will use to evaluate your solution. Knowing these criteria helps you tailor your proposal to meet their exact needs.
The criteria can vary from one company to another, but the most common factors to consider are:
- Features
- Compatibility with existing systems
- Product integrations
- Onboarding assistance
- Pricing
- Return on investment
If the prospective customer does not have decision criteria, you can influence the criteria to align with your company and product strengths.
- Discovery question example: “What is the most important factor you use to evaluate and decide on the best solution? Do you have a specific budget? How do you plan to measure the ROI if you invest in our product or service?”
Decision Process
The decision process outlines the steps and stakeholders involved in the customer’s decision-making journey. Find out the who, when, and how of evaluation, selection, and purchasing of the product.
Understanding this process allows you to align your sales efforts with their timeline and requirements. Furthermore, it will help you avoid losing a sale due to delays. You’ll have a clear picture of what needs to happen from your customer’s side to seal the deal, so you can focus on fulfilling those steps.
- Discovery question example: “What was the process the last time you purchased [similar product]? Can you walk me through your team’s steps to decide on this purchase?”
Identify Pain
Identifying the pain involves pinpointing the critical issues your customer faces. This usually involves technical or business problems that are hurting the company. This is an opportunity to use open-ended questions to dig into the pain’s root cause. During the conversation, you might discover hidden needs that could create another opportunity for your product or service.
- Discovery question example: “What are the main problems or bottlenecks you are experiencing? How is this affecting the business?”
The key here is to be specific. For example, while it’s helpful to know your customer is struggling with poor productivity, it is too vague. But if your customer’s business is facing a 40% decrease in productivity due to outdated collaboration tools, you can align how your product or service can solve this pain point and avoid making false promises.
Champion
The champion is your internal advocate within the customer’s organization who will support and promote your solution. This person is well-respected in the organization and benefits in some way from your and their success. They will help you navigate internal politics and gain buy-in from other stakeholders.
- Discover question example: “Is there someone within your organization who has influence, speaks positively about our solution, and can help us advocate for it internally? Is there anything we are missing as we prepare a business case?”
Based on your initial call, be prepared to determine the ideal number and type of questions. Asking too many questions can feel like an interrogation, while too few might leave you without enough information to present a proper solution to the right people and close a deal. Gauge the customer’s engagement, reception, and responses to find the right balance during the conversation.
Imagine you’re pursuing a manufacturing company interested in your ERP software solution. Here’s how you might apply the MEDDIC process:
- Metrics: You discover that the company wants to increase production efficiency by 20%. Your software’s resource management and automation capabilities can help achieve this.
- Economic buyer: You identify the CRO as the budget-holder and decision-maker who will approve the purchase.
- Decision criteria: The company prioritizes ease of integration with existing systems and robust customer support.
- Decision process: You learn that the decision process involves an RFP, an initial demo, a proof of concept phase, and a final review by the buying committee.
- Identify pain: The company is struggling with outdated software, leading to frequent downtime and communication bottlenecks.
- Champion: You find an IT manager who is enthusiastic about your solution, has excellent internal relationships, will improve their job with the solution, and is willing to advocate for it internally.
Pros and Cons of MEDDIC Framework
The MEDDIC framework is a powerful tool for lead qualification, especially for longer sales cycles with many stakeholders. Let’s discuss the benefits and drawbacks to see if it fits your sales strategy.
Pros
- Targets high-quality leads: When salespeople use MEDDIC to qualify leads, you will zero in on those offering the greatest return. Your time and resources will be spent on sales-ready prospects, leading to a higher closing rate.
- Tailor solutions to customer needs: MEDDIC’s consultative nature helps you better understand your customers’ needs and pain points. This allows you to personalize your solutions to fit them perfectly.
- Sync with the buyer’s process: Understanding the buyer’s purchase decision process is foundational to MEDDIC. Knowing this early on leads to a smoother buying process and fewer misunderstandings.
Cons
- Complex and time-consuming: MEDDIC can be pretty complex and time-consuming. Getting it right requires sales training and practice. The detailed qualification process can slow your sales cycle, making it a poor fit for fast-paced environments.
- Not suitable for all sales environments: MEDDIC might not be the best fit for simpler or high-velocity sales processes. In these cases, the framework’s thoroughness might hinder quick deal closures.
- The framework can be rigid: MEDDIC’s structured approach can sometimes feel inflexible. Sales situations often require flexibility and creativity, and sticking strictly to the framework might limit your ability to adapt, which can be a drawback in dynamic environments.
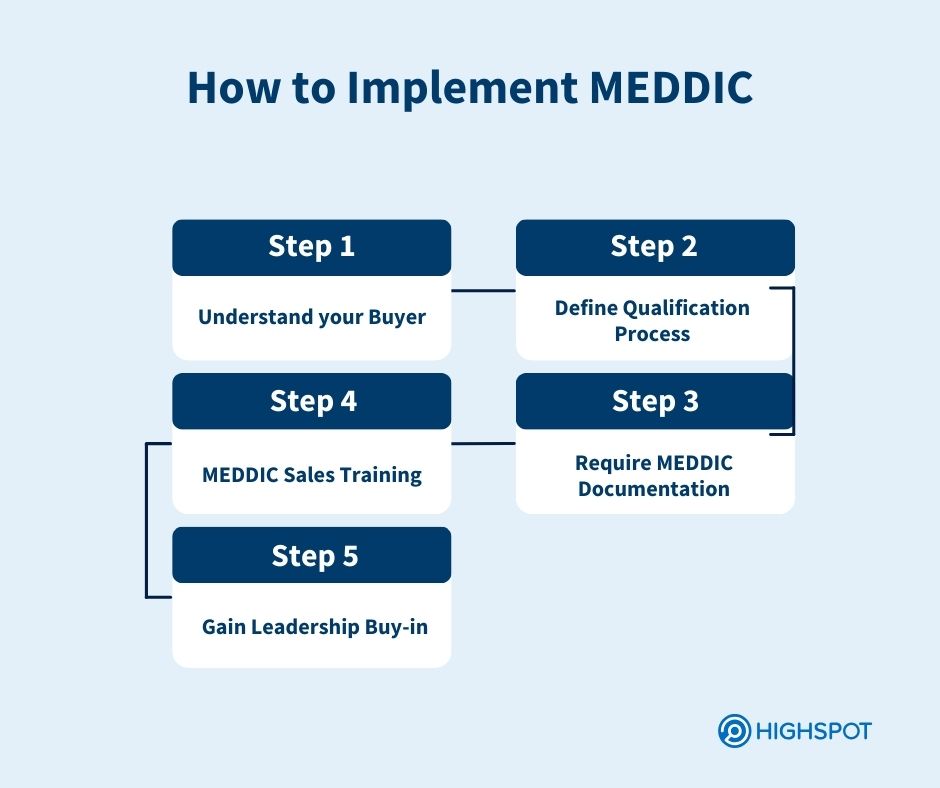
How to Implement the MEDDIC Sales Methodology
Implementing the MEDDIC framework is easier than you might think. It fits right into your existing sales process during the qualification phase. Let’s look at how you can integrate each part of MEDDIC into your current sales efforts.
- Understand your buyers: Work with your marketing team to define buyer personas so that you understand your ideal customer’s roles, challenges, and goals before you talk with them. This will help you identify and engage with the right buyers.
- Define qualification process: Identify gaps and areas for improvement in your current sales qualification process. Then, explore how you can integrate the MEDDIC framework. You can create a flowchart that outlines which resources to use at each step, or conversation guides for sales reps.
- Require MEDDIC documentation: Create a standard MEDDIC template or fields within your CRM to document all customer interactions. Andy Whyte, CEO of MEDDICC, suggests”Existing processes need to shift to embrace MEDDICC; for example, QBR formats should be adapted to include MEDDICC language.”
- Equip sales reps with MEDDIC sales training: Train and coach your sales professionals and sales leaders on the MEDDIC framework. Utilize sales enablement tools to provide real-time support and guidance. Supply them with training materials, customer engagement resources, playbooks, battle cards, sales pitch templates, messaging, and objection-handling strategies.
- Related Resource: Ultimate Guide to Sales Training
- Gain leadership buy-in: Secure major stakeholder support early on. Without this advocacy to promote MEDDIC adoption, you’ll face an uphill battle trying to integrate its usage into sales culture. “Sellers and sales managers are spinning so many plates that adding a new qualification framework plate to their workload without top-to-bottom support stands the chance of being de-prioritized, and subsequently fading away as just another failed initiative,” says Whyte.
Master MEDDIC for Sales Qualification Success
There are many other sales methodologies and frameworks to explore. MEDDIC is a proven framework for B2B enterprise sales and SaaS solutions. If your sales team is struggling to close deals despite a full pipeline, they might be dealing with the wrong prospects. By adopting MEDDIC, your sales funnel can overflow with high-quality leads, your sales organization can thrive, and your reps can close more deals. Aligning with the buyer’s decision-making process and using a solid sales qualification methodology are key steps to achieving sales success.




