Key Takeaways
- A sales model determines how you generate leads, structure your sales organization, and allocate resources.
- Your company’s sales model should match your buyers’ journey and expectations, whether they prefer self-service, personalized outreach, or inbound education.
- Regularly assessing performance and experimenting with hybrid approaches can help you stay competitive and maximize revenue.
If sales strategy was a puzzle, then your sales model would be a corner piece: it helps frame your approach to businesses and determines how the other pieces of your strategy will fit together.
The keystone nature of sales models makes choosing the right one all the more important. In this guide, we’ll detail everything you need to know to pick the perfect sales model for your business.
What Is a Sales Model?
A sales model refers to a business’ overall approach to selling. There is no one right sales model; each organization’s approach will vary depending on its product, industry, and revenue model. Common models include inbound sales, outbound sales, account-based selling, or a combination of multiple models.
Why Do You Need a Sales Model?
Choosing a sales model helps revenue leaders understand how and where they need to invest to grow their business. It’s a roadmap that guides every part of the sales process. A well-defined model focuses efforts, maximizes resources, and ultimately boosts profitability.
Here are reasons why a sales model is important for your business:

Clear Direction and Consistency
A sales model defines the steps required to move a prospect from initial contact to a closed deal. It ensures every sales rep follows a proven process rather than relying on gut instinct. This consistency improves efficiency, reduces mistakes, and helps new team members ramp up faster.
Team Alignment
A sales model ensures that go-to-market teams know how to approach a sale, what the process looks like, and what goals to aim for. This alignment can make a huge difference in performance, especially when everyone’s working toward the same target.
Scalability
When you know what works, you can replicate that success across new teams or product lines. This makes it easier to train new sales reps, expand into new territories, and increase revenue without losing efficiency.
Better Forecasting
A sales model allows you to analyze past performance and make data-driven decisions about future revenue. If you know how many leads typically convert, how long the sales cycle takes, and what steps lead to the highest success rates, you can forecast sales with much greater accuracy.
What’s the Difference Between a Sales Model, Sales Process, and Sales Methodology?
Your sales model determines how you’ll generate leads for your business. Meanwhile, your sales process puts that approach into action, and your sales methodology defines the tactics for engaging and converting leads.
For instance, if you adopted an outbound sales model, you would likely hire a large business development team to perform outreach to buyers and generate sales-qualified leads.
But how do those business development reps know what they need to do to achieve this goal? This is where your sales process comes in. Your sales process should detail step-by-step exactly what this team—and other supporting go-to-market functions—must do to transform potential buyers into customers. To ensure sales reps connect effectively with prospects, your sales methodology will guide them on how they approach conversations, handle objections, and close deals.
Types of Sales Models
Sales models can vary based on your approach to demand generation, sales organization structure, and more. That said, here are a few types of popular sales models to consider:
Inbound Sales

This approach focuses on attracting potential customers by providing valuable content and solutions before they engage with a sales rep. It’s built around educating and nurturing leads until they are ready to buy.
Inbound sales uses digital marketing tactics like search engine optimization (SEO), online advertising, content marketing, and social media to drive traffic. Leads typically come in through blog posts, whitepapers, webinars, or email sign-ups, and sales teams prioritize them based on intent signals like website visits or content downloads. Inbound sales reps then step in once prospects show interest, making the process more consultative and less aggressive.
Outbound Sales
In this model, sales reps go out and find potential buyers. They usually start with a list of prospects who fit a certain profile, even if they haven’t shown interest yet. It’s direct, aggressive, and highly effective when done right.
Sales reps generate leads through cold calls, email, SMS, and networking, targeting prospects based on firmographics, job titles, and industry data. They follow structured sales sequences and use automation tools to streamline outreach. The goal is to start conversations, qualify leads, and move them through the sales funnel.
Account-Based Selling
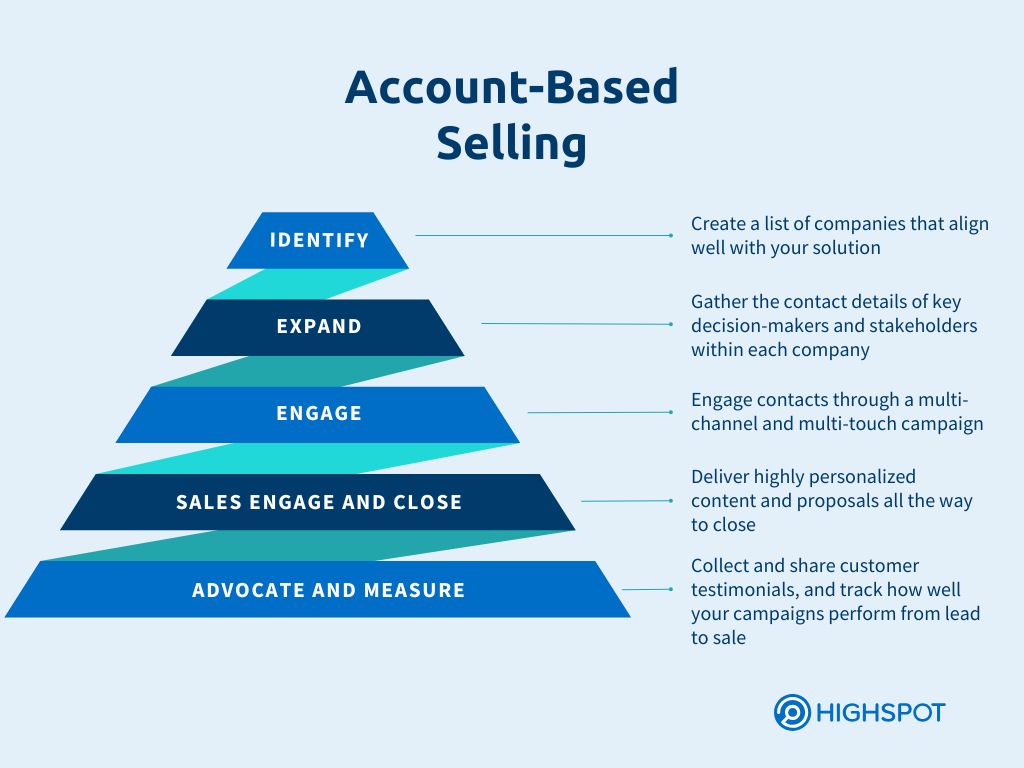
Account-based selling is a laser-focused sales approach in which the entire sales and marketing efforts focus on high-value accounts. Teams take a highly personalized approach, tailoring all elements of the deal to meet the customer’s demands.
Account-based selling requires more extensive research to identify key accounts that match your ideal customer profile. Sales, marketing, and customer success teams work together to create personalized sales pitches, content, and strategies for each account. This approach aims to build deep relationships through multi-touch, multi-channel engagement.
Self-Service Sales
This model allows buyers to self-service the entire sales process on your website, from education to solution purchase. They find, evaluate, and buy products entirely online, often through a product-led growth (PLG) approach that uses free trials or freemium versions to drive adoption.
Chatbots, knowledge bases, and automated onboarding provide support. Meanwhile, in-app upselling and automated marketing workflows help convert users into paying customers.
Whichever sales model you choose, it’s essential to ensure that your pick meets your business objectives. For example, if you are selling a complicated, innovative solution, your business may be best served by an account-based approach, which allows you to build deep connections with buyers. On the other hand, if your solution is easy to purchase, a strong outbound approach to sales may help grow your business quickly.
It is also possible that your sales model will change as your business and offerings evolve. Thus, it can be helpful to continuously evaluate your sales model’s performance.
Finally, many businesses use a combination of models to support different buyer segments — so don’t be afraid to mix and match.
The Ultimate Checklist for Choosing and Implementing a Sales Model
Now that you know what a sales model is, it’s time to decide which one you’ll use. Here are the key factors you’ll want to consider — and how best to put your chosen model into action.
1. Define Your Buyer Personas
First, define your buyer personas. As mentioned above, your sales model will determine how you bring new leads into your sales funnel. But that approach will vary based on who your buyers are and how they want to buy.
For instance, if your buyers tend to be mid-level employees who prefer to do their own research, a self-service model may allow you to quickly and efficiently generate new business. On the flip side, if your buyers are C-suite executives who demand tailored solutions, an account-based approach will serve you better. Knowing who your buyers are will help set you on the right path to choosing a sales model that meets them where they are.
2. Build Your Buyer’s Journey
Next, map out your buyer’s journey. Similar to understanding your buyer personas, a deep understanding of your buyer’s journey will help you determine which sales model is best for your business.
Consider how and where you interact with your buyers throughout the sales cycle, how buyers respond to the resources and tools you provide them, and how long they spend with each. The answers here will reveal buyer expectations, allowing you to select a sales model that is tailored to their preferred experience.
3. Hone Your Sales Strategy
Now it’s time to look at your sales strategy. Think about your product, pricing, and current competitive landscape. What kind of solution are you selling? Who else is selling it? How do they attract buyers? Will you beat them on value or price? How do you expect the market to evolve over time?
The answers to these questions will help you determine which sales model is best for your business. For example, if you are selling a relatively simple solution and a saturated market, you are unlikely to find success with a highly personalized approach to sales — and may very well lose money pursuing an account-based sales model. Here, it would be best to choose a self-service model and double down on customer service and marketing.
4. Uplevel Your Sales Stack
By now, you should have a clear understanding of your buyers and how your company’s sales strategy will move them towards purchase. That means it’s time to consider how you will put your sales model into action with sales technology.
Here, it’s better to match your technology to the sales model you’ve selected rather than the other way around. Consider both current tools and future investments you will need to support your buyer’s journey. Possible technologies to consider include sales engagement tools, a sales enablement platform, a customer relationship management (CRM) solution, and marketing automation software.
Related: The Essential Revenue Tech Stack
5. Enable Your Team’s Success
Once you have your model, strategy, and tech stack in place, focus on putting your sales model into action. The key to successfully implementing a sales model is to enable customer-facing teams with the content, training, and guidance they need to elevate buyer conversations.
What does that look like in practice? You’ll need to support customer-facing teams with robust onboarding and ongoing training, guide their conversations with detailed sales plays, and drive effective interactions with powerful content. Learn more about best practices for building exceptional sales enablement programs with our complete guide.
6. Maximize Your Impact
Finally, think about how you are going to measure the success of your sales model. As we mentioned earlier, it’s possible you may outgrow your initial selection. Alternatively, you may choose to incorporate a second or third sales model to reach new and different buyer personas.
Therefore, it’s essential to continuously examine whether or not your sales model is meeting your goals, and where opportunities for optimization exist. Some key metrics to consider are:
- Revenue by product, segment, territory, or market
- Market penetration
- Acquisition costs
- Average sales cycle length
- Conversation rate by sales funnel stage
These numbers can help you uncover whether or not your sales model is bringing in the business you want it to, or if it’s leaving money on the table that could easily be captured by a different approach.
Delivering Sales Success
Whether you decide to go all-in on account-based sales or prefer an inbound approach, the best practices above are sure to help you secure long-term success.
Looking for more to explore? Our guide to improving your sales process can help you align sales, marketing, and enablement and accelerate your customer’s journey—download your copy today.
This post was originally published in August 2021 and has been updated for accuracy and comprehensiveness.




